|
 |
|
Recent Publications Peptides Containing β-Amino Acid Patterns: Challenges and Successes in Medicinal Chemistry Chiara Cabrele, Tamas A. Martinek, Oliver Reiser, and Lukasz Berlicki, J. Med. Chem., Article ASAP DOI: 10.1021/jm5010896 The construction of bioactive peptides using β-amino acid-containing sequence patterns is a very promising strategy to obtain analogues that exhibit properties of high interest for medicinal chemistry applications. β-Amino acids have been shown to modulate the conformation, dynamics, and proteolytic susceptibility of native peptides. They can be either combined with α-amino acids by following specific patterns, which results in backbone architectures with well-defined orientations of the side chain functional groups, or assembled in de novo-designed bioactive β- or α,β-peptidic sequences. Such peptides display various biological functions, including antimicrobial activity, inhibition of protein–protein interactions, agonism/antagonism of GPCR ligands, and anti-angiogenic activity. Color Test for Selective Detection of Secondary Amines on Resin and in Solution Ulrik Boas and Sahar Mirsharghi, Org. Lett., Article ASAP DOI: 10/1021/ol502936d Publication Date (Web): October 31, 2014 Copyright © 2014 American Chemical Society Resins for solid-phase synthesis give orange to red-brown resin beads selectively when secondary amines are present on the resin when treated with a solution of acetaldehyde and an Fmoc-amino acid in NMP. The method shows good specificity and gives colorless beads when exposed to a variety of other functional groups. Furthermore, the acetaldehyde/Fmoc-amino acid method can be used as a selective colorimetric test for secondary amines in solution. Peptide YY, neuropeptide Y and corticotrophin-releasing factor modulate gastrointestinal motility and food intake during acute stress Forbes SC, Cox HM., Neurogastroenterol. Motil., 2014, 26, 1605-14. DOI: 10.1111/nmo.12428 Peripheral neuropeptide Y (NPY) provides protection against the endocrine, feeding and gastrointestinal (GI) responses to stress; however, it is not yet established how it interacts with corticotrophin-releasing factor (CRF) to mediate these effects. Peptide YY (PYY) also has significant roles in GI motility and food intake but little is known about its role in stress responses.
Tumor-Penetrating iRGD Peptide Inhibits Metastasis Sugahara KN, Braun GB, de Mendoza TH, Kotamraju VR, French RP, Lowy AM, Teesalu T, Ruoslahti E., Mol. Cancer Ther., 2014 Nov 12. pii: molcanther.0366.2014. [Epub ahead of print] Tumor-specific tissue-penetrating peptides deliver drugs into extravascular tumor tissue by increasing tumor vascular permeability through interaction with neuropilin (NRP). Here we report that a prototypic tumor-penetrating peptide iRGD (amino acid sequence: CRGDKGPDC) potently inhibits spontaneous metastasis in mice. The anti-metastatic effect was mediated by the NRP-binding RXXK peptide motif (CendR motif), and not by the integrin-binding RGD motif. iRGD inhibited migration of tumor cells and caused chemorepulsion in vitro in a CendR- and NRP-1-dependent manner. The peptide induced dramatic collapse of cellular processes and partial cell detachment, resulting in the repellent activity. These effects were prominently displayed when the cells were seeded on fibronectin, suggesting a role of CendR in functional regulation of integrins. The anti-metastatic activity of iRGD may provide a significant additional benefit when this peptide is used for drug delivery to tumors. Copyright © 2014, American Association for Cancer Research. A novel antibacterial peptide active against peach crown gall (Agrobacterium tumefaciens) isolated from cyanide-tolerant actinomycetes G19. Wang S, Ji J, Ma H, Liu Z., World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014 Oct 31. [Epub ahead of print] DOI: 10.1007/s11274-014-1765-2 An antimicrobial peptide was extracted from the antagonistic actinomycetes G19. It was designated as G19-F. By using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, the molecular weight of G19-F was determined. The primary structure of the antimicrobial peptide was determined using N-terminal sequencing and mass spectrometry. Results showed that the peptide had eleven amino acids, with the sequence D-V-C-D-G-G-D-G-D-E-D, and a calculated molecular mass of 1,096 Da. G19-F showed antimicrobial activity against peach crown gall caused by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. The antimicrobial peptide maintained its activity after being heated to 100 °C and exhibited stability from pH 4 to 10. Its activity has also remained after ultraviolet irradiation. The mechanism by which G19-F inhibits A. tumefaciens was to increase permeability of the cell membrane and destroy the cell wall structure. Furthermore, as a novel peptide, it has a potential for cure A. tumefaciens infection. The discovery of Hsp70 domain with cell-penetrating activity. Komarova EY, Meshalkina DA, Aksenov ND, Pchelin IM, Martynova E, Margulis BA, Guzhova IV., Cell Stress Chaperones, 2014 Nov 12. [Epub ahead of print] Chaperone Hsp70 can cross the plasma membrane of living cells using mechanisms that so far have not received much research attention. Searching the part of the molecule that is responsible for transport ability of Hsp70, we found a cationic sequence composed of 20 amino acid residues on its surface, KST peptide, which was used in further experiments. We showed that KST peptide enters living cells of various origins with the same efficiency as the full-length chaperone. KST peptide is capable of carrying cargo with a molecular weight 30 times greater than its own into cells. When we compared the membrane-crossing activity of KST peptide in complex with Avidin (KST-Av complex) with that of similarly linked canonical TAT peptide, we found that TAT peptide penetrated SK-N-SH human neuroblastoma cells at a similar rate and efficiency as the KST peptide. Furthermore, KST peptide can carry protein complexes consistingof a specific antibody coupled to the peptide through the Avidin bridge. An antibody to Hsp70 delivered to SK-N-SH cells with high expression level of Hsp70 reduced the protective power of the chaperone and sensitized the cells to the pro-apoptotic effect of staurosporine. We studied the mechanisms of penetration of KST-Av and full-length Hsp70 inside human neuroblastoma SK-N-SH and human erythroleukemia K-562 cells and found that both used an active intracellular transport mechanism that included vesicular structures and negatively charged lipid membrane domains. Competition analysis of intracellular transport showed that the chaperone reduced intracellular penetration of KST peptide and conversely KST peptide prevented Hsp70 transport in a dose-dependent manner. A cell-penetrating peptide analogue, P7, exerts antimicrobial activity against Escherichia coli ATCC25922 via penetrating cell membrane and targeting intracellular DNA. Li L, Shi Y, Cheng X, Xia S, Cheserek MJ, Le G., Food Chem, 2015, 166, 231-9. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.05.113. The antibacterial activities and mechanism of a new P7 were investigated in this study. P7 showed antimicrobial activities against five harmful microorganisms which contaminate and spoil food (MIC=4-32 μM). Flow cytometry and scanning electron microscopy analyses demonstrated that P7 induced pore-formation on the cell surface and led to morphological changes but did not lyse cell. Confocal fluorescence microscopic observations and flow cytometry analysis expressed that P7 could penetrate the Escherichia coli cell membrane and accumulate in the cytoplasm. Moreover, P7 possessed a strong DNA binding affinity. Further cell cycle analysis and change in gene expression analysis suggested that P7 induced a decreased expression in the genes involved in DNA replication. Up-regulated expression genes encoding DNA damage repair. This study suggests that P7 could be applied as a candidate for the development of new food preservatives as it exerts its antibacterial activities by penetrating cell membranes and targets intracellular DNA. Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. |
|
β-Amino Acids 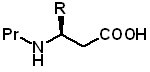 Beta-amino acids and beta-homoamino acids incorporated into peptides can increase resistance to digestive enzymes, improve selectivity, enhance potency and increase metabolic stability, making them interesting drug candidates. Antibactials, opioid peptide analogs, and drugs for cancer treatment are a few examples of the applications of β-peptides. (K. Stachowiak, et al., J Med Chem. 1979, 22, 1128-30; KM Bromfield, et al., Chem Biol Drug Des. 2006, 68, 11-9; S Nordhoff, et al., Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009, 19, 6340-5; MA Ondetti, SL Engel, J Med Chem. 1975, 18, 761-3; D Janke, et al., Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2011, 19, 7236).
Methylated Lysines Methylation of lysine residue sidechains plays a regulatory role in histones and other proteins. Study of these regulatory processs and the enzymes involved requires suitable substrates, analogs and model peptides. AAPPTec supplies modified lysine derivatives suitable for preparing peptide substrate analogs of these regulatory sites. For information on utilizing methylated lysine derivates in solid phase peptide synthesis, see our Technical Bulletin.
.jpg)
2 HCl.jpg)
3Cl.jpg)
Apex 396
The Apex 396 is the premier productivity tool. Capable of preparing a few peptides or up to 96 separate peptides at the same time, the Apex 396 is ideal for SAR studies, optimization studies, drug discovery, and small scale peptide production.
Neuropeptide Y
Neuropeptide Y is a neurotransmitter in the brain and central nervous system. It plays an important role in the hypothalamic control of body energy. It also influences stress response, circadian rhythms and cardiovascular function. Neuropeptide Y increases food consumption and stimulates fat build up in the abdomen. Overexpression of neuropeptide Y in mice seems to lead to diabetes.
PEG Linkers Unlike hydrocarbon linkers that are hydrophobic, PEG linkers are hydrophilic and help improve the solubility characteristics of hydrophobic peptides or peptides labeled with hydrophobic tags. AAPPTec PEG linkers have uniform established structures and sizes, allowing you to incorporate them and obtain well-defined products.
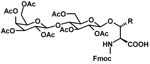
For additional PEG products from AAPPTec, go to the PEGylation Reagents page of our website www.aapptec.com. Glycoamino Acids Glycosylation is one of the most common post-translational modifications of proteins. It is crucial for signaling and regulatory events and plays a role in the transport of proteins through the endoplasmic reticulum and membranes. Glycoproteins play an essential role in cell-cell recognition and in the docking of bacteria and viruses onto cells. They also play an important role in fertilization (Talbot P.; et al. Biol. Reprod., 2003, 68, 1-9), brain development (Varki A.; et al. Glycobiology, 1993, 3, 97-130), the endocrine system (Rudd P.M.; et al. Science, 2001, 291, 2370-6) and the immune system (Bertozzi C.R.; et al. Science, 2001, 291, 2357-64). 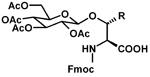
|
 |
UPCOMING EVENTS |
|
|
February 2015 Informex February 3-6 |
 |
