|
 |
|
Featured Articles An Fmoc compatible, O to S shift-mediated procedure for the preparation of C-terminal thioester peptides F Liu, J P Mayer, J. Org. Chem., Just Accepted Manuscript DOI: 10.1021/jo4015112 Publication Date (Web): September 3, 2013 Copyright ę 2013 American Chemical Society We report a concise 2-hydroxy-3-mercapto-propionic acid (Hmp) / 2-methylpiperidine (2-MP) based Fmoc chemistry procedure to prepare the C-terminal Hmp peptides, which serve as the precursors of peptide C-terminal thioesters. The subsequent O to S acyl shift and thiol-exchange mediated thioester conversion of the crude precursor peptides can be accomplished smoothly under mild conditions to provide the desired peptide thioesters with good yield and high quality. This is a highly adaptable approach and we envision its broad application in the preparation of thioester peptides. Stapled α-helical peptide drug development: A potent dual inhibitor of MDM2 and MDMX for p53-dependent cancer therapy. YS Chang, B Graves, V Guerlavais, C Tovar, K Packman, KH To, KA Olson, K Kesavan, P Gangurde, A Mukherjee, T Baker, K Darlak, C Elkin, Z Filipovic, FZ Qureshi, H Cai, P Berry, E Feyfant, XE Shi, J Horstick, DA Annis, AM Manning, N Fotouhi, H Nash, LT Vassilev, TK Sawyer, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013, 110, E3445-54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1303002110. Stapled α-helical peptides have emerged as a promising new modality for a wide range of therapeutic targets. Here, we report a potent and selective dual inhibitor of MDM2 and MDMX, ATSP-7041, which effectively activates the p53 pathway in tumors in vitro and in vivo. Specifically, ATSP-7041 binds both MDM2 and MDMX with nanomolar affinities, shows submicromolar cellular activities in cancer cell lines in the presence of serum, and demonstrates highly specific, on-target mechanism of action. A high resolution (1.7-┼)
X-ray crystal structure reveals its molecular interactions with the target protein MDMX, including multiple contacts with key amino acids as well as a role for the hydrocarbon staple itself in target engagement. Most importantly, ATSP-7041 demonstrates robust p53-dependent tumor growth suppression in MDM2/MDMX-overexpressing xenograft cancer models, with a high correlation to on-target pharmacodynamic activity, and possesses favorable pharmacokinetic and tissue distribution properties. Overall, ATSP-7041 demonstrates in vitro and in vivo proof-of-concept that stapled peptides can be developed as therapeutically relevant inhibitors of protein-protein interaction and may offer a viable modality for cancer therapy.
Effects of the Arg-Pro and Gly-Gly-Nle Moieties on Melanocortin-1 Receptor Binding Affinities of α-MSH Peptides J Yang, L Liu, Y Miao, ACS Med. Chem. Lett., Article ASAP The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of the -Arg-Pro- (RP) and -Gly-Gly-Nle- (GGNle) moieties on the melanoma targeting and clearance properties of 99mTc-peptides. We synthesized four new peptides {Ac-GGNle-CCEHdFRWC-NH2, Ac-GGNle-CCEHdFRWCRP-NH2, Ac-CCEHdFRWC-NleGG-NH2, and Ac-CCEHdFRWCRP-NleGG-NH2} and determined their melanocortin-1 (MC1) receptor binding affinities in B16/F1 melanoma cells. Then we further examined the biodistribution properties of 99mTc-Ac-GGNle-CCEHdFRWCRP-NH2 and 99mTc-Ac-CCEHdFRWCRP-NleGG-NH2 in B16/F1 melanoma-bearing C57 mice. Overall, the -RP- moiety was critical for retaining low nanomolar MC1 receptor binding affinity. The deletion of the -RP- moiety dramatically reduced the receptor binding affinities of the peptides. The N-terminus was a better position than C-terminus for the -GGNle- moiety in retaining the lower renal and liver uptake. High melanoma uptake coupled with fast urinary clearance of 99mTc-Ac-GGNle-CCEHdFRWCRP-NH2 provided a new insight into the design of new α-melanocyte stimulating hormone (α-MSH) peptides. A Novel Antimicrobial Peptide from Skin Secretions of the Tree Frog Theloderma kwangsiensis. H Yan, Y Liu, J Tang, G Mo, Y Song, X Yan, L Wei, R Lai, Zoolog Sci. 2013, 30, 704-9. Most of amphibians belonging to family Rhacophoridae live in arboreal habitats. A large number of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) have been identified from amphibian skins. No antimicrobial peptide from Rhacophoridae amphibians has been reported. In this study, we purified and characterized a novel antimicrobial peptide, pleurain-a1-thel from skin secretions of the tree frog, Theloderma kwangsiensis. Its amino acid sequence was determined as RILTMTKRVKMPQLYKQIVCRLFKTC by Edman degradation, mass spectrometry analysis and cDNA cloning. There are two cysteines, which form an intra-molecular disulfide bridge, in the sequence of pleurain-a1-thel. Pleurain-a1-thel exerted potential antimicrobial activities against wide spectrum of microorganisms, including Gram-negative and -positive bacteria and fungi. It exerted little hemolytic activity in human or rabbit red cells. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of antimicrobial peptide from Rhacophoridae amphibians. Linaclotide-a Novel Secretagogue in The Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Constipation and Chronic Idiopathic Constipation. S Sharma, T Sharma, R Dhingra, P Tomar, S Singh, M Malhotra, TR Bhardwaj, Mini Rev Med Chem. 2013, 13, 1685-90. doi: 10.2174/1389557511313110011 Irritable bowel syndrome with constipation (IBS-C) and chronic idiopathic constipation (CIC) are highly prevalent gastrointestinal disorders. Traditional symptoms based therapies had somewhat limited success and efficacy in addressing the disorders. Recently, linaclotide emerged as novel peptide capable of improving abdominal symptoms in patients suffering from IBS-C and CIC. Guanylate cyclase C (GC-C) receptor a multi domain protein, found to be molecular target for linaclotide which acts by activating GC-C receptor on the apical surface of intestinal epithelial cells. Binding of linaclotide to GC-C receptor triggers the elevation of second messenger cGMP that elicits fluid secretion into intestinal cells which play a critical role in maintaining homeostasis through cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR). Data from Phase II and III clinical trials demonstrated that linaclotide seems to produce a statistically significant increase in stool frequency, improved straining, decreased abdominal pain and discomfort. Monosubstituted alkenyl amino acids for peptide "stapling" DJ Yeo, SL Warriner, AJ Wilson. Chem Commun (Camb). 2013, 49, 9131-3 DOI: 10.1039/c3cc45231j Alkenylglycine amino acids were assessed as potential candidates for hydrocarbon stapling and shown to be effective in stapling of the BID BH3 peptide.
Vasonatrin peptide, a novel protector of dopaminergic neurons against the injuries induced by n-methyl-4-phenylpyridiniums. HK Zhao, BY Chen, R Chang, JB Wang, F Ni, L Yang, XC Dong, SH Sun, G Zhao, W Fang, DR Ma, XL Wang, J Yu. Peptides. 2013 Sep 18. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2013.09.005. [Epub ahead of print] Vasonatrin peptide (VNP), a novel manmade natriuretic peptide, is known as a cardiovascular active substance. However its neuroeffects are largely unknown. Here, cultured dopaminergic neurons from ventral mesencephalon of mouse were exposed to N-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+), and the effects of VNP on the neurotoxicity of MPP+ were investigated. As a result, MPP+ caused injuries in the dopaminergic neurons. VNP significantly reduced the cytotoxicity of MPP+ by increasing axon number and length of dopaminergic neurons, and by enhancing the cell viability. Also, the MPP+-induced depolymerization of -β-Tubulin III was attenuated by the treatment of VNP. In addition, VNP significantly increased the intracellular levels of cGMP. These effects of VNP were mimicked by 8-br-cGMP (a cell-permeable analog of cGMP), whereas inhibited by HS-142-1 (the antagonist of the particulate guanylyl cyclase-coupled natriuretic peptide receptors), or KT-5823 (a cGMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor). Taken together, VNP attenuates the neurotoxicity of MPP+ via guanylyl cyclase-coupled NPR/cGMP/PKG pathway, indicating that VNP might be a new effective reagent in the treatment of neuron degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson's disease (PD). Modulation of taste responsiveness by the satiation hormone peptide YY. MS La Sala, MD Hurtado, AR Brown, DV Bohˇrquez, RA Liddle, H Herzog, S Zolotukhin, CD Dotson. FASEB J. 2013 Sep 16. [Epub ahead of print] DOI: 10.1096/fj.13-228064 It has been hypothesized that the peripheral taste system may be modulated in the context of an animal's metabolic state. One purported mechanism for this phenomenon is that circulating gastrointestinal peptides modulate the functioning of the peripheral gustatory system. Recent evidence suggests endocrine signaling in the oral cavity can influence food intake (FI) and satiety. We hypothesized that these hormones may be affecting FI by influencing taste perception. We used immunohistochemistry along with genetic knockout models and the specific reconstitution of peptide YY (PYY) in saliva using gene therapy protocols to identify a role for PYY signaling in taste. We show that PYY is expressed in subsets of taste cells in murine taste buds. We also show, using brief-access testing with PYY knockouts, that PYY signaling modulates responsiveness to bitter-tasting stimuli, as well as to lipid emulsions. We show that salivary PYY augmentation, via viral vector therapy, rescues behavioral responsiveness to a lipid emulsion but not to bitter stimuli and that this response is likely mediated via activation of Y2 receptors localized apically in taste cells. Our findings suggest distinct functions for PYY produced locally in taste cells vs. that circulating systemically. Identification of bitter peptides in whey protein hydrolysate. X Liu, D Jiang, DG Peterson DG., J Agric Food Chem. 2013 Sep 3. [Epub ahead of print] Bitterness of whey protein hydrolysates (WPH) can negatively impact product quality and limit utilization in food and pharmaceutical applications. Four main bitter peptides were identified in a commercial WPH by means of sensory-guided fractionation techniques that included ultrafiltration and offline two-dimensional reverse phase chromatography. LC-TOF-MS/MS analysis revealed the amino acid sequences of the bitter peptides were YGLF, IPAVF, LLF and YPFPGPIPN that originated from α-lactalbumin, β-lactoglobulin, serum albumin, and β-casein respectively. Quantitative LC/MS/MS analysis reported the concentrations of YGLF, IPAVF, LLF and YPFPGPIPN to be 0.66, 0.58, 1.33 and 2.64g/kg powder, respectively. Taste recombination analysis of an aqueous model consisting of all 4 peptides was reported to explain 88% of the bitterness intensity of the 10% WPH solution. Preclinical development of a novel class of CXCR4 antagonist impairing solid tumors growth and metastases L Portella, R Vitale, S De Luca, C D'Alterio, C Ieran˛, M Napolitano, A Riccio, MN Polimeno, L Monfregola, A Barbieri, A Luciano, A Ciarmiello, C Arra, G Castello, P Amodeo, S Scala, PLoS One. 2013 Sep 13;8(9):e74548. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074548. The CXCR4/CXCL12 axis plays a role in cancer metastases, stem cell mobilization and chemosensitization. Proof of concept for efficient CXCR4 inhibition has been demonstrated in stem cell mobilization prior to autologous transplantation in hematological malignancies. Nevertheless CXCR4 inhibitors suitable for prolonged use as required for anticancer therapy are not available. To develop new CXCR4 antagonists a rational, ligand-based approach was taken, distinct from the more commonly used development strategy. A three amino acid motif (Ar-Ar-X) in CXCL12, also found in the reverse orientation (X-Ar-Ar) in the vMIP-II inhibitory chemokine formed the core of nineteen cyclic peptides evaluated for inhibition of CXCR4-dependent migration, binding, P-ERK1/2-induction and calcium efflux. Peptides R, S and I were chosen for evaluation in in vivo models of lung metastases (B16-CXCR4 and KTM2 murine osteosarcoma cells) and growth of a renal cells xenograft. Peptides R, S, and T significantly reduced the association of the 12G5-CXCR4 antibody to the receptor and inhibited CXCL12-induced calcium efflux. The four peptides efficiently inhibited CXCL12-dependent migration at concentrations as low as 10 nM and delayed CXCL12-mediated wound healing in PES43 human melanoma cells. Intraperitoneal treatment with peptides R, I or S drastically reduced the number of B16-CXCR4-derived lung metastases in C57/BL mice. KTM2 osteosarcoma lung metastases were also reduced in Balb/C mice following CXCR4 inhibition. All three peptides significantly inhibited subcutaneous growth of SN12C-EGFP cancer cells. A novel class of CXCR4 inhibitory peptides was discovered. Three peptides, R, I and S inhibited lung metastases and primary tumor growth and will be evaluated as anticancer agents.
|
|
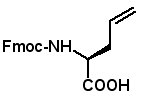
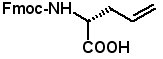
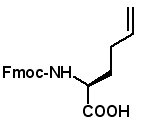
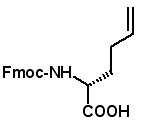
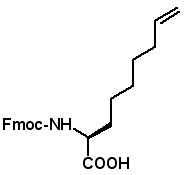
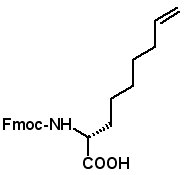
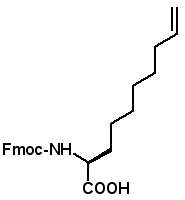
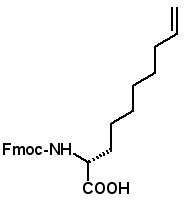
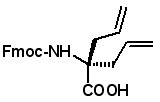
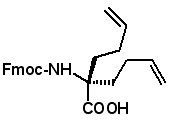
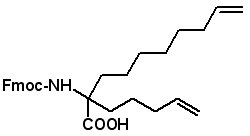
Proceedings of the 23rd APS Now Available The Proceedings of the 23rd APS are now available in PDF format. The file can be downloaded from the website www.5z.com/23APS. Availability of the printed book will be announced on the same site. New Building Blocks for Stapled Peptides Stapled peptides incorporate a hydrocarbon bridge that helps form the peptide into an α-helical structure. Stapled peptides are attractive drug leads for several reasons: • Stapled peptides may have better cell permeation properties than linear peptides. AAPPTec has expanded its selection of alkenyl amino acid building blocks for preparing stapled peptides. Fmoc-(2S)-Allylglycine
Fmoc-(2R)-Allylglycine
Fmoc-(2S)-(3'-butenyl)glycine
Fmoc-(2R)-2-(3'-butenyl)glycine
Fmoc-(2R)-2-(4'-pentenyl)glycine
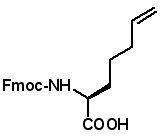
Fmoc-(2S)-(5'-hexenyl)glycine
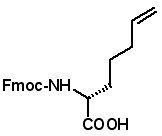
Fmoc-(2R)-(5'-hexenyl)glycine
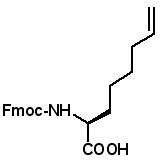
Fmoc-(2S)-(6'-heptenyl)glycine
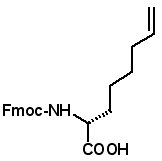
Fmoc-(2R)-(6'-heptenyl)glycine
Fmoc-(2S)-(7'-octenyl)glycine
Fmoc-(2R)-(7'-octenyl)glycine
Fmoc-2,2-bis(2-propenyl)glycine
Fmoc-2,2-bis(3-butenyl)glycine
Fmoc-2-amino-2(pent-4-enyl)dec-9-enoic acid
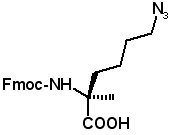
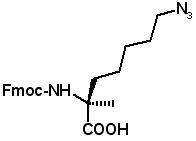
These amino acids allow stapled peptides to be prepared by "click" chemistry. (S)-N-Fmoc-2-(4'-azidobutyl)alanine
(S)-N-Fmoc-2-(5'-azidobutyl)alanine
(S)-N-Fmoc-2-(6'-azidobutyl)alanine
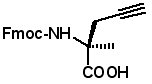
(S)-N-Fmoc-2-(2'-propynyl)alanine
(R)-N-Fmoc-2-(2'-propynyl)alanine
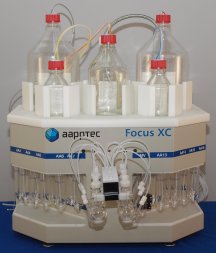
Fluorescent Labeling Reagents AAPPTec now offers fluorescent labeling reagents, including Focus XC Solid Phase Peptide Synthesizer The Focus XC is the ideal research and production peptide synthesizer. It can synthesize up to six different peptides at the
same time in scales from milligrams to grams. The Focus XC is easy to operate. The easy to use software allows novices to prepare high quality peptides, but also offers flexibility for
experts to develop new protocols and optimize the synthesis of difficult peptides.
• Up to 6 reaction vessels to prepare up to 6 different peptides at the same time
AAPPTec's online peptide catalog contains over 2100 peptide products at very competitive prices. The peptide catalog includes peptides in these classes:
Vasonatrin peptide is a chimera consisting of C-type natriuretic peptide plus the five C-terminal residues of atrial natriuretic peptide. It has the venodilating actions of CNP, the natriuretic renal actions of ANPand arterial vasodilating actions that are not associated with either ANP or CNP. It is also shown to protect dopaminergic neurons against injuries induced by N-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium compounds. C-M Wei, et al., J.Clin. Invest., 1998, 92, 2048; HK Zhao, et al., Peptides, 2013, Sept 18 [Epub ahead of print]
|
 |
UPCOMING EVENTS |
|
|
November 2013 4th Modern Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis Symposium November 2-4 |
 |