|
 |
|
Featured Articles Selectively N-Methylated Soluble IAPP Mimics as Potent IAPP Receptor Agonists and Nanomolar Inhibitors of Cytotoxic Self-Assembly of Both IAPP and Aβ40 LM Yan, A Velkova, M Tatarek-Nossol, G Rammes, A Sibaev, E Andreetto, M Kracklauer, M Bakou, E Malideli, B Göke, J Schirra, M Storr, A Kapurniotu, Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2013 Aug 19. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201302840. [Epub ahead of print] The selective incorporation of N-methyl groups in the highly amyloidogenic and cytotoxic sequence of the type 2 diabetes islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) generates a unique class of soluble and nontoxic IAPP mimics. These polypeptides combine potent IAPP receptor agonism with nanomolar-affinity inhibitory potential on the amyloid formation and cell-damaging effects of both IAPP and the Alzheimer's β-amyloid peptide (Aβ40). Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 protects human islets against cytokine-mediated β-cell dysfunction and death: a proteomic study of the pathways involved D Rondas, M Bugliani, W D'Hertog, K Lage, M Masini, E Waelkens, P Marchetti, C Mathieu, L Overbergh, J. Proteome Res., Just Accepted Manuscript DOI: 10.1021/pr400527q Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) has been shown to protect pancreatic β-cells against cytokine-induced dysfunction and destruction. The mechanisms through which GLP-1 exerts its effects are complex and still poorly understood. The aim of this study was to analyze the protein expression profiles of human islets of Langerhans treated with cytokines (IL-1β and IFN-γ) in the presence or absence of GLP-1, by two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis and subsequent protein interaction network analysis, in order to understand the molecular pathways involved in GLP-1-mediated β-cell protection. Co-incubation of cytokine-treated human islets with GLP-1 resulted in a marked protection of β-cells against cytokine-induced apoptosis and significantly attenuated cytokine-mediated inhibition of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. The cytoprotective effects of GLP-1 coincided with substantial alterations in the protein expression profile of cytokine-treated human islets, illustrating a counteracting effect on proteins from different functional classes such as actin cytoskeleton, chaperones, metabolic proteins and islet regenerating proteins. In summary, GLP-1 alters in an integrated manner protein networks in cytokine-exposed human islets while protecting them against cytokine-mediated cell death and dysfunction. These data illustrate the beneficial effects of GLP-1 on human islets under immune attack, leading to a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms involved, a prerequisite for improving therapies for diabetic patients. Local control of cis-peptidyl-prolyl bonds mediated by CHπ interactions: The Xaa-Pro-Tyr motif H K Ganguly, H Kaur, G Basu, Biochemistry, Just Accepted Manuscript, DOI: 10.1021/bi4007918 Compared to generic peptide bonds, the peptidyl-prolyl bond shows a high propensity for the cis-conformer. The presence of a sequence-contiguous aromatic (Aro) residue can further stabilize the cis-conformer, as observed for the Aro-Pro motif. The cis-propensity of the reverse sequence motif, Pro-Aro, is not so well understood, especially the effect of N-capping the Pro-Aro motif with different amino acid residues. From a comparative NMR study on two peptide series with the general sequence, Ac-Xaa-Pro-Tyr-NH2 and Ac-Xaa-Pro-Ala-NH2, we present a relative thermodynamic scale that reflects how the nature of Xaa sidechain influences the cis-propensity of the Xaa-Pro-Tyr motif, with Gly, Pro and Ala at position Xaa exhibiting the highest enhancement of the cis peptidyl-prolyl population. We also show that CHπ interaction, operative between Xaa and Tyr is responsible for the enhanced cis-population. However, the mere presence of the CHπ interaction does not guarantee that the peptidyl-prolyl bond will have a higher cis-content in Xaa-Pro-Tyr compared to that in Xaa-Pro-Ala. Xaa-dependent intra-molecular interactions present in Xaa-transPro-Tyr can nullify favorable CHπ interactions in Xaa-cisPro-Tyr. The relative cis-peptidyl-prolyl stabilizing propensities of Xaa (Xaa-Pro-Tyr) in proteins and in our peptide series show strong linear correlation except when Xaa is aromatic. We also explore the sequence motif Xaa-Pro-Gly-Tyr and show that mediated by a Pro-Tyr CHπ interaction, the cis-peptidyl-prolyl bond in the motif is stabilized when Xaa is Pro. Click chemistry in Peptide-based drug design H Li, R Aneja, I Chaiken, .Molecules, 2013, 18, 9797-817. DOI: 10.3390/molecules18089797. Click chemistry is an efficient and chemoselective synthetic method for coupling molecular fragments under mild reaction conditions. Since the advent in 2001 of methods to improve stereochemical conservation, the click chemistry approach has been broadly used to construct diverse chemotypes in both chemical and biological fields. In this review, we discuss the application of click chemistry in peptide-based drug design. We highlight how triazoles formed by click reactions have been used for mimicking peptide and disulfide bonds, building secondary structural components of peptides, linking functional groups together, and bioconjugation. The progress made in this field opens the way for synthetic approaches to convert peptides with promising functional leads into structure-minimized and more stable forms. High pH Reversed-phase Chromatography as a Superior Fractionation Scheme Compared to Off-Gel Isoelectric Focusing for Complex Proteome Analysis. Stein DR, Hu X, McCorrister SJ, Westmacott GR, Plummer FA, Ball TB, Carpenter MS. Tandem mass spectrometry is the technology of choice for analyzing complex protein mixtures. However, due to the intrinsic complexity and dynamic range present in higher eukaryotic proteomes, pre-fractionation is an important step to maximize the number of proteins identified. Off-gel isoelectric focusing (OG-IEF) and high pH reversed-phase (Hp-RP) column chromatography have both been successfully utilized as a first dimension peptide separation technique in shotgun proteomic experiments. Here, a direct comparison of the two methodologies was performed on ex-vivo peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) lysate. In 12-fraction replicate analysis, Hp-RP resulted in more peptides and proteins identified than OG-IEF fractionation. Distributions of peptide isoelectric points and hydropathy did not reveal any appreciable bias in either technique. Resolution, defined here as the ability to limit a specific peptide to one particular fraction, was significantly better for Hp-RP. This leads to a more uniform distribution of total and unique peptides for Hp-RP across all fractions collected. These results suggest that fractionation by Hp-RP over OG-IEF is the better choice for typical complex proteome analysis. This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved. Comparative characterization and cytotoxicity study of TAT-peptide as potential vectors for siRNA and Dicer-substrate siRNA. Katas, M Abdul Ghafoor Raja, LC Ee, Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2013 Aug 21. [Epub ahead of print] DOI:10.3109/03639045.2013.828222 Recently, a newly discovered Dicer-substrate siRNA (DsiRNA) demonstrates higher potency in gene silencing than siRNA but both suffer from rapid degradation, poor cellular uptake and chemical instability. Therefore, Tat-peptide was exploited to protect and facilitate their delivery into cells. In this study, Tat-peptide was complexed with siRNA or DsiRNA through simple complexation. The physicochemical properties (particle size, surface charge and morphology) of the complexes formed were then characterized. The ability of Tat-peptide to carry and protect siRNA or DsiRNA was determined by UV-Vis spectrophotometry and serum protection assay, respectively. Cytotoxicity effect of these complexes was assessed in V79 cell line. siRNA-Tat complexes had particle size ranged from 186±17.8 to 375±8.3 nm with surface charge ranged from -9.3±1.0 to +13.5±1.0 mV, depending on the Tat-to-siRNA concentration ratio. As for DsiRNA-Tat complexes, the particle size was smaller than the ones complexed with siRNA, ranging from 176±8.6 to 458±14.7 nm. Their surface charge was in the range of +27.1±3.6 to +38.1±0.9 mV. Both oligonucleotide (ON) species bound strongly to Tat-peptide, forming stable complexes with loading efficiency of more than 86%. These complexes were relatively non cytotoxic as the cell viability of 90% was achieved. In conclusion, Tat-peptide has a great potential as siRNA and DsiRNA vector due to the formation of stable complexes with desirable physical characteristics, low toxicity and able to carry high amount of siRNA or DsiRNA.
JS Wattez, R Ravallec, B Cudennec, C Knauf, P Dhulster, P Valet, C Breton, D Vieau, J Lesage, Apelin is an enteric peptide that exerts several digestive functions such as stimulation of cell proliferation and cholecystokinin (CCK) secretion. We investigated using murine enteroendocrine cell line (STC-1) and rats if apelin-13 stimulates both CCK and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) secretions. We demonstrated that, in vitro and in vivo, apelin-13 increases the release of these two hormones in a dose-dependent manner. Present data suggest that apelin may modulate digestive functions, food intake behavior and glucose homoeostasis via apelin-induced release of enteric CCK but also through a new incretin-releasing activity on enteric GLP-1.
Engineered knottin peptide enables noninvasive optical imaging of intracranial medulloblastoma. SJ Moore SJ, MG Hayden Gephart, JM Bergen, YS Su, H Rayburn, MP Scott, JR Cochran, Central nervous system tumors carry grave clinical prognoses due to limited effectiveness of surgical resection, radiation, and chemotherapy. Thus, improved strategies for brain tumor with visualization and targeted treatment are critically needed. We demonstrate that mouse cerebellar medulloblastoma (MB) can be targeted and illuminated with a fluorescent, engineered cystine knot (knottin) peptide that binds with high affinity to αvβ3, αvβ5, and α5β1 integrin receptors. This integrin-binding knottin peptide, denoted EETI 2.5F, was evaluated as a molecular imaging probe in both orthotopic and genetic models of MB. Following tail vein injection, fluorescence arising from dye-conjugated EETI 2.5F was localized to the tumor compared with the normal surrounding brain tissue, as measured by optical imaging. The imaging signal intensity correlated with tumor volume. Due to its unique ability to bind to α5β1 integrin, EETI 2.5F showed superior in vivo and ex vivo brain tumor imaging contrast compared with other engineered integrin-binding knottin peptides and with c(RGDfK), a well-studied integrin-binding peptidomimetic. Next, EETI 2.5F was fused to an antibody fragment crystallizable (Fc) domain (EETI 2.5F-Fc) to determine if a larger integrin-binding protein could also target intracranial brain tumors. EETI 2.5F-Fc, conjugated to a fluorescent dye, illuminated MB following i.v. injection and was able to distribute throughout the tumor parenchyma. In contrast, brain tumor imaging signals were not detected in mice injected with EETI 2.5F proteins containing a scrambled integrin-binding sequence, demonstrating the importance of target specificity. These results highlight the potential of using EETI 2.5F and EETI 2.5-Fc as targeted molecular probes for brain tumor imaging.
The Role of Obestatin in Glucose and Lipid Metabolism. E Gargantini, C Grande, L Trovato, E Ghigo, R Granata, Horm Metab Res. 2013 Aug 15. [Epub ahead of print] DOI: 10.1055/s-0033-1351325 Obestatin is a 23 amino acid peptide encoded by the ghrelin gene, which, like ghrelin, is mainly produced by the stomach, as well as by a wide range of other tissues. Obestatin remains a controversial peptide, as the initial finding of its binding to the orphan receptor GPR39 and the inhibitory effect on food intake has been questioned. In fact, to date, its biological effects are still largely unknown, although it is becoming clear that obestatin is a pleiotropic hormone, exerting a variety of effects in different cell types and tissues. Indeed, besides regulating cell proliferation and survival, obestatin has been shown to regulate glucose and lipid metabolism, both in vitro, in pancreatic β-cells and adipocytes, and in vivo in rodents. Furthermore, its positive effects on glucose homeostasis, combined with the anti-inflammatory actions, make this peptide appealing as a candidate for treating metabolic disorders such as insulin resistance and diabetes.
|
|
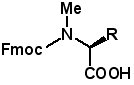
Fmoc-N-Methyl Amino Acids Introducing N-methyl amino acids in a peptide can produce analogs with valuable properties. A recent publication (Yan, et al, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, Aug 19. Epub. ahead of print) reports that selective incorporation of N-methyl groups into type 2 diabetes islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) produces analogs with potent IAPP receptor agonism and inhibitory effects on amyloid formation and cell-damaging effects of IAPP and β-amyloid peptide. AAPPTec offers a large variety of N-methyl amino acids suitably protected for solid phase peptide synthesis.
Glucagon-Like Peptide I Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) increases insulin production while decreasing glucagon production. It also increases the insulin sensitivity of alpha-cells and beta-cells. GLP-1 has been shown to protect pancreatic β-cells against cytokine-induced dysfunction and destruction. Toft-Nielsen M., Madsbad S., Holst J., J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 3853–60; Meier J. et al. Crit.Care Med. 2004, 32, 848–51; Drucker D.J. Gastroenterology, 2002, 122, 531-44; Janssen P., Rotondo A., Mule F., Tack J., Aliment. Pharm. Therap., 2012, 37, 18-36.
Click Chemistry Building Blocks
Click chemistry is a convenient, high yield method for attaching tags and labels, conjugating peptides to proteins or other biomolecules, and for forming cyclic peptide structures. Recently, Liskamp and co-workers reported using Lys(N3) in a Ru(II) catalyzed double cyclization of a hexapeptide (J. Zhang, J. Kemmink, D.T.S. Rijkers, R.M.J. Liskamp, Chem. Commun., 2013, 49, 4498-4500).
Spirit HPLC Columns High pH reversed phase chromatography is becoming a powerful and highly useful technique in proteome analysis. It has been successfully used as a first dimension peptide separation technique in shotgun proteomic experiments. AAPPTec’s Spirit peptide columns and protein columns are ideally suited for high pH separations. Spirit columns are specially manufactured to provide stability, reproducibility and high resolution at high pH. In fact, Spirit HPLC columns provide high performance and stability over a wide range of pH conditions, from very low to high. For more information about Spirit HPLC columns, go to the Spirit HPLC Column page of the AAPPTec web site or send an e-mail to info@aapptec.com. Custom Peptides AAPPTec chemists have over 25 years experience producing high quality peptides. By utilizing their experience, AAPPTec provides timely and very competitively priced custom peptide products to academic and pharmaceutical laboratories worldwide. TAT Peptides TAT peptide is a cell penetrating peptide derived from the HIV-1 TAT protein. This arginine-rich peptide penetrates plasma membranes directly and has been shown to promot the entry of nucleic acids into several types of cells. (Torchilin, VP; et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2001, 98, 8786; Sharkar, T; et al., Nucl. Acids Res., 2005, 33, 143; Katads, H; et al., Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2013 Aug 21. [Epub ahead of print] ).
Apelin was identified by M. Fujino and co-workers in 1998 [Tatemoto, K et al. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 251, 471]. It plays different functions throughout the body. It participates in the control of blood pressure [Lee, DK et al. J. Neurochem. 2000, 74, 34] by producing a hypotensive effect. Studies suggest that apelin signaling and angiotensin II signaling balance to maintain steady blood pressure [Ishida, J et al. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 26274]. In the heart, apelin is a highly potent stimulator of cardiac contractility [Szokodi, I et al. Circ. Res. 2002, 91, 434; Berry, MF et al. Circulation 2004, 110, II187; Ashley, EA et al. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 65, 73]. In the brain, apelin increases water intake [Lee, DK et al. J. Neurochem. 2000, 74, 34] and decreases the production of vasopressin, an antidiuretic hormone [De Mota, N et al. Neuroendocrinology 2000, 72, 400]. Recently, apelin was shown to stimulate both cholecystokinin and glucagon-like peptide 1 secretion in rodents [Wattez, JS et al. Peptides 2013 Aug 14. Epub ahead of print].
The synthesis of peptides with complex disulfide bridging, such as the knottin peptide, requires the use of many different cysteine derivative side chains that can be selectively removed to allow step-wise formation of the complex disulfide bridges.
AAPPTec offers many cysteine derivatives from preparing peptides with complex disulfide bridging.
.jpg)
Obestatin Obestatin has been shown to antagonize growth hormone secretion and food intake induced by ghrelin. (Zhang, JV; et al. Science, 2005, 310, 996; Hassouna, R; et al. J. Neuroendocrinol., 2010, 22, 793). Recently, obestatin has been shown to regulate glucose and lipid metabolism (Gargantini, E, et al. Horm Metab Res. 2013 Aug 15. [Epub ahead of print]).
Using the Focus XC (6), you can synthesize up to 6 different sequences at the same time.
|
 |
UPCOMING EVENTS |
|
|
October 2013 8th Annual Peptide Therapeutics Symposium October 24-25 La Jolla, California November 2013 4th Modern Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis Symposium November 2-4 |
 |